
An engaged citizenry is usually seen as an indication of a wholesome democracy. Excessive ranges of political and civic participation enhance the chance that residents' voices will probably be heard in necessary debates and supply a level of legitimacy to democratic establishments. Nevertheless, in lots of nations all over the world, a lot of the general public is disconnected from politics.
Survey carried out in 14 nations
| Argentina | Kenya |
| Brazil | Mexico |
| Greece | Nigeria |
| Hungary | Philippines |
| Indonesia | Poland |
| Israel | South Africa |
| Italy | Tunisia |
Supply: World Attitudes Survey, Spring 2018.
To raised perceive public attitudes towards civic engagement, the Pew Analysis Middle carried out in-person surveys in 14 nations spanning a variety of political techniques. The examine, carried out in collaboration with the Middle for Strategic and Worldwide Research (CSIS) as a part of its Worldwide Consortium on Closing Civic Area (iCon), contains nations from Africa, Latin America, Europe, the Center East and Southeast Asia. As a result of the examine doesn’t cowl each area, it can’t mirror the globe as a complete. However with 14,875 individuals in such all kinds of nations, it stays a helpful snapshot of necessary, cross-national patterns in civic life.
The survey exhibits that, along with voting, comparatively few folks additionally participate in different types of political and civic participation. Nevertheless, some varieties of engagement are extra widespread amongst younger folks, these with increased training, political leftists and social community customers. And sure points—notably well being care, poverty, and training—are extra probably than others to stimulate political motion. Listed below are eight key takeaways from the survey, which was carried out via in-person interviews from Could 20 to August 12, 2018.
Most individuals vote, however different types of participation are far much less widespread. Throughout the 14 nations surveyed, a mean of 78% stated they’d voted no less than as soon as up to now. One other 9% say they may vote sooner or later, whereas 7% say they’d by no means vote.
With no less than 9 out of ten respondents reporting having voted up to now, voter turnout is highest in three of the 4 nations with obligatory voting (Brazil, Argentina and Greece). Voter turnout is equally excessive in each Indonesia (91%) and the Philippines (91%), two nations the place there aren’t any obligatory voting legal guidelines.
The bottom share is in Tunisia (62%), which has held solely two nationwide elections for the reason that 2011 Jasmine Revolution, which toppled long-serving President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali and sparked Arab Spring protests throughout the Center East.
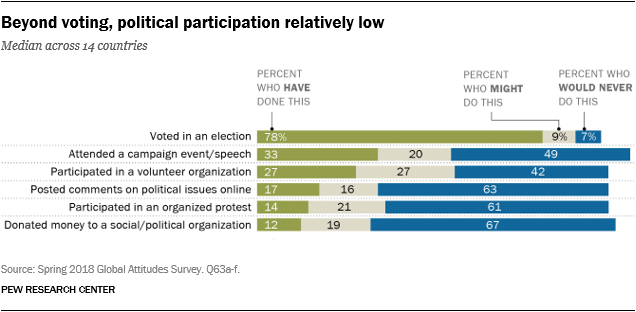
Attending a political marketing campaign occasion or speech is the second commonest type of participation amongst respondents – a mean of 33% have accomplished so no less than as soon as. Fewer folks say they’re concerned in volunteer organizations (27% on common), submit political feedback on-line (17%), take part in an organized protest (14%), or donate cash to a social or political group (12%) ).
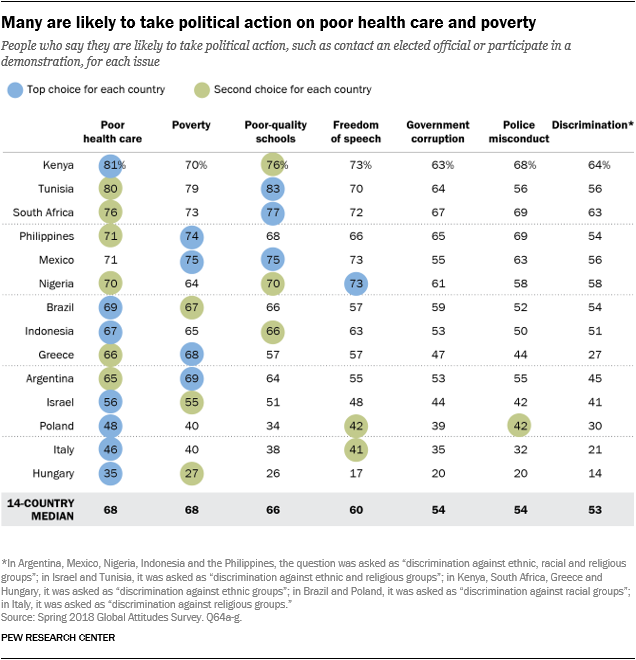
Well being care, poverty and training are the primary motivators for political engagement. When requested what varieties of points would possibly immediate them to take political motion, resembling contacting an elected official or attending an indication, folks in 13 out of 14 nations listed poor well being care as both their first or second selection among the many subjects examined to. Many additionally think about poverty and poor faculty high quality to be the 2 most important issues. General, individuals are barely much less prone to say that the opposite issues examined might encourage them to take motion. An exception is freedom of expression, which is an important motivating subject in Nigeria and second in Italy and Poland (the place it’s tied with police misconduct as second).
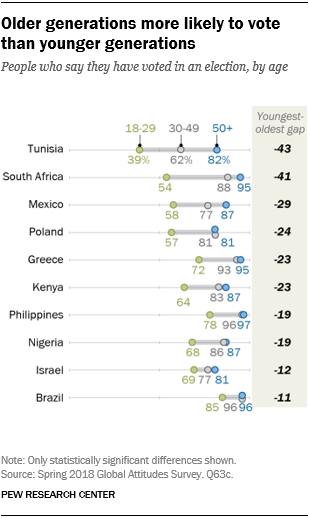
Younger folks vote much less usually. In ten of the nations surveyed, folks aged 50 and over are extra probably than these aged 18 to 29 to say they’ve voted in no less than one election. The hole between the oldest and youngest respondents who voted is greater than 40 share factors in Tunisia and South Africa and greater than 20 share factors in Mexico, Poland, Greece and Kenya.
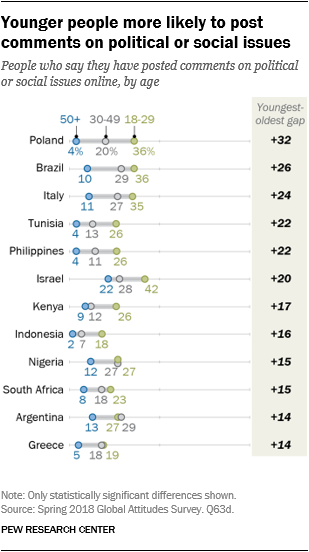
Nevertheless, younger individuals are extra prone to take part on-line. In 12 of the 14 nations surveyed, folks ages 18 to 29 are extra probably than older adults to submit on-line feedback about social or political points. For instance, 36% of Poles aged 18 to 29 have posted their views on-line, in comparison with simply four% of these over 50.
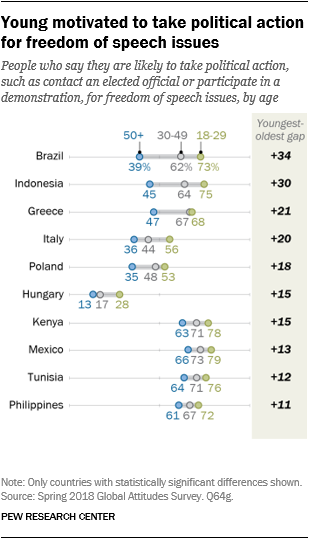
Younger individuals are additionally extra motivated by quite a lot of points. Freedom of expression is an efficient instance: in ten nations, 18- to 29-year-olds are extra probably than folks over 50 to say they’d take political motion on the difficulty of freedom of expression. In Brazil, 73% of adults underneath 30 say freedom of expression might encourage them to turn out to be politically energetic, in comparison with 39% of these over 50. Younger individuals are additionally extra prone to take motion on discrimination in ten nations. There are additionally important age variations in poor faculty high quality, police misconduct, poverty, authorities corruption and poor well being care.
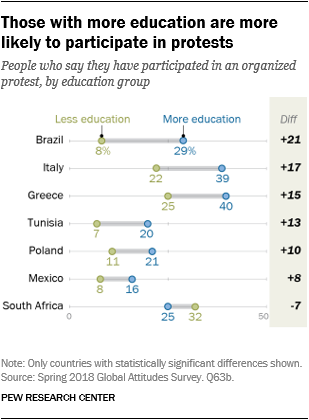
There’s a shut connection between training and political participation. In 13 nations, folks with increased training usually tend to publish their views on-line. Seven nations usually tend to have donated cash to a political or social group. And in six nations they’re extra probably to participate in political protests. About three in ten Brazilians with increased ranges of training (29%) have participated in a protest, in comparison with simply eight% of these with much less training.
Folks with increased training are additionally persistently extra prone to be motivated by sure points. That is notably true for freedom of expression: in 11 nations, folks with increased ranges of training usually tend to say they is likely to be motivated to turn out to be politically energetic on freedom of expression points. Poverty is the one drawback the place there are comparatively few variations between folks with increased training and folks with much less training.
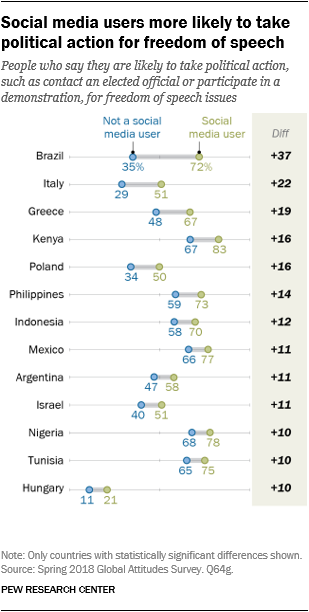
Social media use is related to better engagement with points. Individuals who use on-line social networking websites are notably vulnerable to be politically engaged on the entire subjects coated within the survey. For instance, in 13 out of 14 nations, individuals who use social media are extra probably than those that don't to say they could take political motion on free speech. As a gaggle, social networkers are usually youthful and extra educated than those that don’t have interaction in social networking.
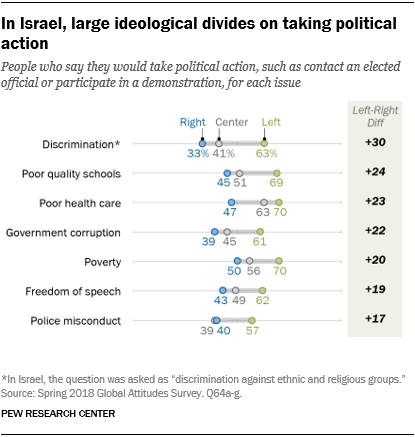
In some instances, folks on the political left usually tend to take motion than on the proper. In eight of the nations examined, respondents have been requested to position themselves on a left-right ideological scale. In a number of nations, these on the left aspect of the political spectrum are extra probably to participate in protests and are motivated to take part by problems with freedom of expression and police misconduct. Israel stands out as a rustic the place ideological variations are notably widespread – each subject examined is extra motivating for these on the left than for these on the proper. Totally 63% of Israelis on the political left, for instance, say they’re prone to take political motion on discrimination, in comparison with simply 33% on the proper.

